Much of my additional information comes
from the internet reference
site called "Wikipedia" which is at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
If you like the resource you may think about donating towards the upkeep of this site.
Wikipedia (pronunciation
by the non-profit Wikimedia Foundation. Its name is a portmanteau of the words wiki
(a technology for creating collaborative websites) and encyclopedia.Wikipedia's
10 million articles have been written collaboratively by volunteers
around the world, and almost all of its articles can be edited by anyone who can access the Wikipedia website.[6]
Launched in 2001 by Jimmy Wales and Larry Sanger,[7]it is currently the largest and most popular[1] general reference work on the Internet.[8][9][10]
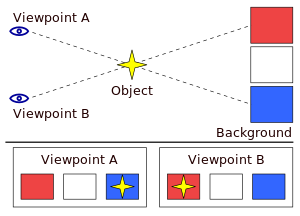
Parallax Error
Parallax is an apparent displacement or
difference of orientation of an object
viewed along two different lines of sight, and is measured by the angle
or semi-angle of
inclination between those two lines
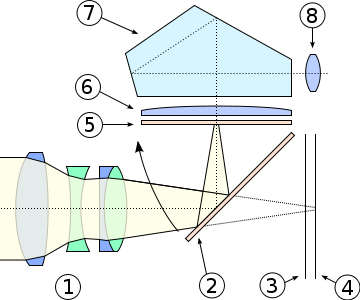
Digital single-lens reflex camera.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_single-lens_reflex_camera
A digital
single-lens reflex camera
(digital SLR or DSLR) is a digital camera that uses
a mechanical mirror system and pentaprism to direct light from the lens to an optical
viewfinder on the back of the camera.
Compact
digital still camera
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_Camera
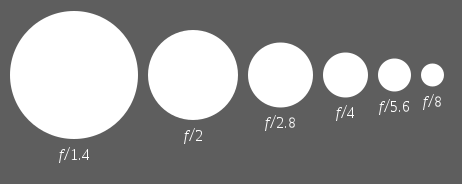
F-number
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/F_stop
In optics, the f-number
(sometimes called focal
ratio, f-ratio, or relative aperture[1]) of an optical system expresses
the diameter of the entrance pupil in terms of the focal length of the lens; in simpler terms,
the f-number is the focal length divided by the "effective" aperture
diameter.
It is a dimensionless
number that is
a quantitative measure of lens speed,
an important concept in photography.
Depth of field
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Depth_of_Field
In optics, particularly as it relates
to film and photography, the depth of field (DOF) is the portion of a scene
that appears sharp
in the image. Although a lens can precisely focus at only one
distance, the decrease in
sharpness is gradual on either side of the focused distance, so that
within the DOF, the
unsharpness is imperceptible under normal viewing conditions.
NB.These pictures are also courtesy of Wikipedia
 F22 = Very deep field
F22 = Very deep field
F2.8 Very shallow field

At f/32,
the background is distracting.

At f/5.6,
the flowers are isolated from the background.
Metering mode
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metering_mode
In photography,
the metering
mode refers to
the way in which a
camera determines the exposure.
Exposure compensation
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exposure_compensation
Exposure compensation
is a technique for adjusting the exposure indicated by a photographic
exposure
meter, in
consideration of factors that may cause the indicated exposure to
result in
a less-than-optimal image. Factors considered may include unusual
lighting distribution,
variations within a camera system, filters, non-standard processing,
or intended underexposure or overexposure. Cinematographers may also
apply exposure
compensation for changes in shutter
angle or film speed, among other factors.

No comments:
Post a Comment